
I know it’s not popular amongst advocates of the so-called Mediterranean diet, but there is a fact about olive oil that has been established in peer-reviewed literature for some time now: Olive oil is NOT as good for you as you might have thought.
So why is it that those eating the Mediterranean diet have had such a reputation for longevity and good health? The answer lies in what other foods are eaten and, equally importantly, which other foods are not eaten (processed junk food).
The traditional Mediterranean diet is fading away as the Western diet – also known as the Standard American Diet (SAD) – spreads its influence across the continent.
But before the golden arches threatened to overshadow the Acropolis, the traditional Mediterranean diet was largely plant-based, consisting of vegetables, fruits, nuts, beans, whole grains, pasta, olive oil, wine, and very small amounts of fish, eggs, dairy, and meats. And while heart disease mortality was lower when compared to the UK and USA, for instance, the benefits seem to have been conferred primarily by a high percentage of plant content, the regular consumption of nuts and an avoidance of sugary/fatty desserts, with fruit being the common after-dinner treat.
And, while compared to the modern Western diet, the Mediterranean diet has been shown to be better at cutting heart attack risk, it has not demonstrated the health-promoting power of a purely whole food plant-based diet – whether the latter is with or without SOS (added sugar, oil and salt). As you will know by now, the WFPB diet is the only known diet that has been clinically proven to reverse heart disease.
A major problem with the Mediterranean diet is that it includes three elements that are associated with inflammation and its many harmful consequences in the body:
- refined grains (pasta and breads),
- animal products, and
- olive oil,
and it is the olive oil that concerns us here.
A publication in the Nutrition, Metabolism & Cardiovascular Diseases journal pretty much sums up its findings in the title of the study:
“Olive, soybean and palm oils intake have a similar acute detrimental effect over the endothelial function in healthy young subjects.”
Objective
Their objective was to evaluate the acute effect of the ingestion of large amounts of olive, soybean and palm oils, fresh and at two different deep-fry levels, on the glucose and lipid profiles and endothelial function.
Method
Subjects were randomly given a potato soup meal containing one of three different vegetable oils (olive, soybean and palm). Flow-mediated vasodilation (FMD) was performed and blood samples taken to establish the lipid profiles and plasma glucose levels.
Results
All types of oil tested (including olive oil) resulted in a similar acute endothelial impairment.
Conclusions of the Study
“No difference was found in the acute adverse effect of the ingestion of different vegetable oils on the endothelial function. All the vegetable oils, fresh and deep-fried, produced an increase in the triglyceride plasma levels in healthy subjects.”
Blog Contents
What are Endothelial Cells and Why are they so Important?
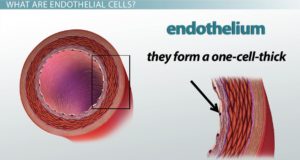 The endothelial cell layer is a one-cell thick layer within the inner surface of our blood vessels. These cells are of vital importance for vascular health and their damage is what leads to the development of CVD (cardiovascular disease).
The endothelial cell layer is a one-cell thick layer within the inner surface of our blood vessels. These cells are of vital importance for vascular health and their damage is what leads to the development of CVD (cardiovascular disease).
When you eat the typical Western diet you develop intracellular adhesion molecules – causing blood to flow like Velcro. This results in the LDL particles in the bloodstream burrowing into the subendothelial compartment. The so-called “bad” LDL cholesterol gets oxidised by free radicals in our diet into small hard dense LDL molecules, so our body sends out messengers called chemokines that recruit white blood cells (monocytes) to sort them out.
These monocytes follow the LDL into the subendothelial compartment in order to scavenge for the LDL particles. Once inside the subendothelial compartment, these monocytes are referred to as macrophages as they try to mop up and clear away all the LDL particles.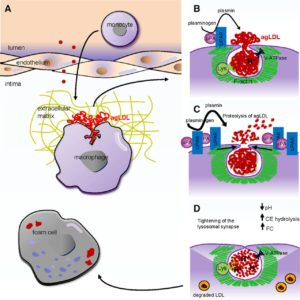
The macrophages get bigger and bigger as they absorb the LDL particles and they then change their name again and become known as foam cells.
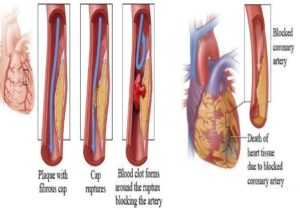
These foam cells are the really dangerous particles because they release some unpleasant enzymes called metalloproteinases which then gradually erode the plaque on the endothelial cell.
The cap over the plaque is very thin and once it ruptures, the plaque content then oozes out and causes a plaque clot.
The plaque clot then grows and spreads out over the inner diameter (lumen) of the blood vessel and this results in something you really don’t want to happen: the downstream heart muscle loses its blood supply.
The result is that the heart muscle dies. This whole nasty process is thought to account for around 90% of all heart attacks.
Is it Too Late for Sufferers of Heart Disease?
Fortunately, it is not too late, even if plaques have formed. The cap over the plaque can be strengthened and, if it is sufficiently strong, you become “heart attack proof” as Dr Esselstyn says, but only if you change to a whole food plant based diet.
How is Nitric Oxide Involved?
Initially it was called EDRF, but had its name changed because it was then discovered that EDRF was in fact a gas – nitric oxide (chemical symbol NO), discovered by Furchgott et al in 1998, for which they received the Nobel Prize.
The Functions of NO
- It prevents intracellular contents from getting sticky – makes the blood flow like Teflon instead of Velcro.
- NO is the strongest vasodilator in the body. When you run for a bus or climb the stairs, it’s the NO produced by your endothelial cells that dilates the blood vessels and allows you to increase activity level without passing out.
- It prevents the vessel walls from getting stiff, thickened or inflamed – hence preventing hypertension.
- Sufficient NO will prevent blockages or plaques building up on the surface of the endothelium.
- NO will prevent the artery wall from “migrating” into the plaque.
- NO can destroy the foam cells (referred to by Dr Esselstyn as “Darth Vaders”).
What is the Flow-Mediated Dilation Test?
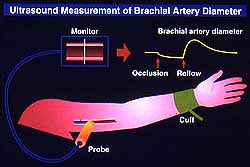
If you take an ultrasound probe, place it over the brachial artery at the elbow, you can get a readout of the diameter of the artery.
You then put a blood pressure cuff on the upper arm, inflate it above systolic blood pressure and leave it there for 5 mins.
During this time, there is zero blood flow to the forearm and hand (a weird sensation to say the least).
You then release the cuff and once again measure the new diameter of the brachial artery.
In a normal artery it should immediately increase by 30%.
Enter Dr Robert Vogel…
Dr Vogel did a brilliant study by taking a number of healthy young people to McDonald’s and splitting them into two groups.
He gave one group cornflakes and measured their dilation response. It was normal.
He gave the other group hash browns and sausages. Their brachial arteries could not dilate normally – even after two hours. The endothelial cells’ ability to make nitric oxide was so damaged that they could not dilate the artery. They were tested on an off into the evening, by which time they started to recover full function as the evening progressed.
A One-Off or Chronic Problem?
It is not a good idea to repeat this test, but people do – millions of them, day in day out, week in week out, for years and decades. The next day it’s egg and bacon or cappuccino and brioche for breakfast, ham and cheese sandwich or chicken salad for lunch, take-away Chinese for dinner. What was an acute reaction becomes a regular, chronic health threat.
This is why, in the 21st century, by the time our children are leaving school, they already have the foundation for cardiovascular disease.
Best Advice
If you really want to protect yourself as much as possible against these cardiovascular events, do all you can to optimise the health of your endothelial cells.
To do this, start by always avoiding the following:
- Oils – no matter whether it’s olive oil, corn oil, soybean oil, safflower oil, sunflower oil, canola oil, palm oil, oil in a crisp/chip, oil in a cracker, oil in bread, oil in a salad dressing.
- Anything with a face or that had a mother – no matter whether it’s fish or fowl, beef or pork, turkey or chicken, cream or milk, cheese or butter, yogurt or ice cream.
- Anything with added sugar – no matter whether it’s organic muscovado sugar, molasses, honey, juices* (orange, apple etc), maple syrup or agave syrup.
All of these injure endothelial cells to some extent; and you don’t need a history of cardiovascular disease to already have it developed within your body – in one study, 57% of men who experienced sudden cardiac death had zero history of coronary heart disease.
* Eating an apple or an orange is not the same thing as drinking fruit juices. The fructose is bound with the fibre. But when you make orange juice or apple juice, the sugar is free, goes into your gut and is immediately absorbed, injuring your liver, promoting protein glycation, and injuring those precious and delicate endothelial cells.
I know it is difficult to consider such dramatic changes, but remember that we live in a nutritionally toxic environment in the 21st century, where the all-pervasive “normal” diet is something that has never existed on Earth before. Nowadays, a person who insists on eating a truly healthy diet will feel and probably be treated like an alien from a distant galaxy.

[qsm quiz=2]
References:
Rueda-Clausen CF, Silva FA, Lindarte MA, Villa-Roel C, Gomez E, Gutierrez R, Cure-Cure C, López-Jaramillo P. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2007 Jan;17(1):50-7. Epub 2006 Mar 20. Olive, soybean and palm oils intake have a similar acute detrimental effect over the endothelial function in healthy young subjects.
Esselstyn C. Prevent Card. 2001; 4: 171–177. Resolving the coronary artery disease epidemic through plant-based nutrition.
Esselstyn C, Ellis S, Medendorp S, Crowe T. J Fam Pract. 1995; 41(6):560–568. A strategy to arrest and reverse coronary artery disease: a 5-year longitudinal study of a single physician’s practice.
Go A, Mozaffarian D, Roger V, Benjamin E, et al. Circulation 2013; 127: 6–245. doi: 10.1161. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2013 update: a report from the American Heart Association.
van Dam RM, Willett WC. Nutr, Metab Cardiov Dis. 2007; 17(1): 50–57. Unmet potential for cardiovascular disease prevention in the United States.
Ryan A. Harris, Steven K. Nishiyama, D. Walter Wray, and Russell S. Richardson. Hypertension. 2010 May; 55(5): 1075–1085. Published online 2010 Mar 29. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.110.150821. Ultrasound Assessment of Flow-Mediated Dilation: A Tutorial.
Vogel RA, Corretti MC, Plotnick GD. Am J Cardiol. 1997 Feb 1;79(3):350-4. Effect of a single high-fat meal on endothelial function in healthy subjects.
Kannel WB, Doyle JT, McNamara PM, Quickenton P, Gordon T. Circulation. 1975;51:606–13. Precursors of sudden coronary death: Factors related to the incidence of sudden death.
Please click here if you wish to unsubscribe. Remember, you can resubscribe at any time.